
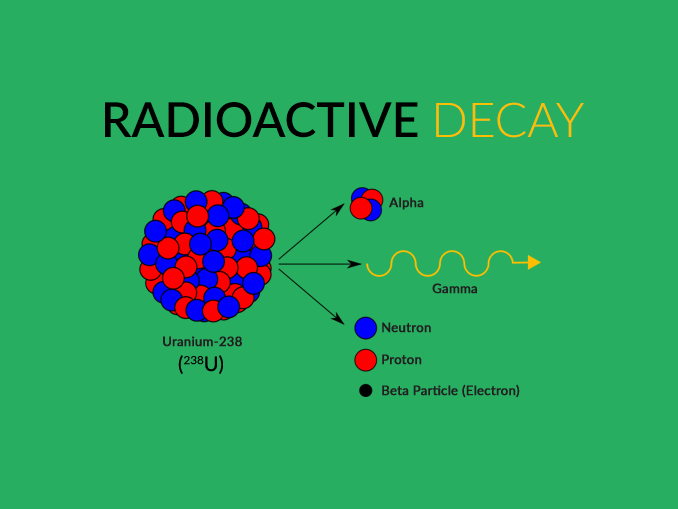
For shielding, you can consider barriers made with concrete or lead. To avoid radioactivity, you need to go far away or distance yourself far away from the source of the radioactivity. Some of the elements like Strontium-90 have a half-life of 30 years. Some of the radioactive elements disappear within minutes or even hours, but some of their decay very slowly. How long does it take for radioactivity to disappear? So, to attain stability, radioactivity occurs. The nucleus present in the atom remains in a very exciting stage. The radioactivity occurs due because the atoms remain in a very unstable state. It is highly dangerous hence, it needs to be used under careful observation.The three types of radioactivity decay are Alpha, Beta, and Gamma decay.It helps in the diagnosis and therapy of various diseases Radioactivity is widely applied in the medical world.As the nucleus is left in an excited state, it tries to become stable, so it releases a gamma-ray photon this helps the atom to lower its energy and attain stability.It occurs after one of the decays, like the alpha or the beta decay, takes place.Gamma decay is considered those particles which can penetrate the matter at the greatest distance.Beta decay is again differentiated into two types - Beta minus and Beta plus.

Beta-decay occurs with a nucleus having too many neutrons and too many protons the protons or neutrons transform into another.It is emitted from the nucleus hence, it has a daughter nucleus (A - 4, Z - 2).Alpha decay (A = 4, Z = 2) is those particles that can penetrate the matter at the shortest distance.The types of radioactive decays are as follows: Later additional types of decay were discovered. All these types were named after the ability to penetrate matter. There are mainly three types of radioactive decay that were discovered first. Half life refers to the time taken by the radioactive sample to fall to half its original value. The rate of decay of a group of atoms can be anticipated by the half-lives or decay constants. Radioactive decay is one of the ways this excess energy is expelled. Radiation occurs when an unstable, high-energy nucleus of an element releases some of that energy to get to a more stable state (similar to when you consume way too much sugar and need to work off all of that energy!).

We hear about the concept of 'radiation' all the time, especially in medical terminology. Since Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity, the SI unit of radioactivity is becquerel (Bq).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
